Visual Studio Code
Enable Visual Studio Code to seamlessly identify the correct runtime for your project, letting you leverage the security and compliance features inherent in the ActiveState project within your integrated development environment (IDE).
Before you begin
Before using your ActiveState project’s Python interpreter in your VS Code environment, make sure the following conditions are met:
- The State Tool is installed on your local machine and is updated to V.36 or later. To update your State Tool, open your command terminal and enter
state update. If you have installed the State Tool after opening VS Code you will need to restart VS Code for the changes to take effect. - You have checked out your Python project from the ActiveState Platform.
- You have the newest version of the VS Code Python extension installed (version 2023.5.10672245 or later). Click here to learn more about updating VS Code extensions.
The following will help you integrate Visual Studio Code with your ActiveState project.
Setting up your IDE
Begin by creating a Python file in your project, or opening an existing Python file. If this is a new file you may be prompted to select an interpreter, or if it is an existing file you can select a new interpreter using the VS Code Command Palette.
To access the “Select Interpreter” drop-down from the Command Palette
- Press Shift + Ctrl + P on Windows and Linux or Shift + Cmd + P on macOS
- Click “Python: Select Interpreter”.
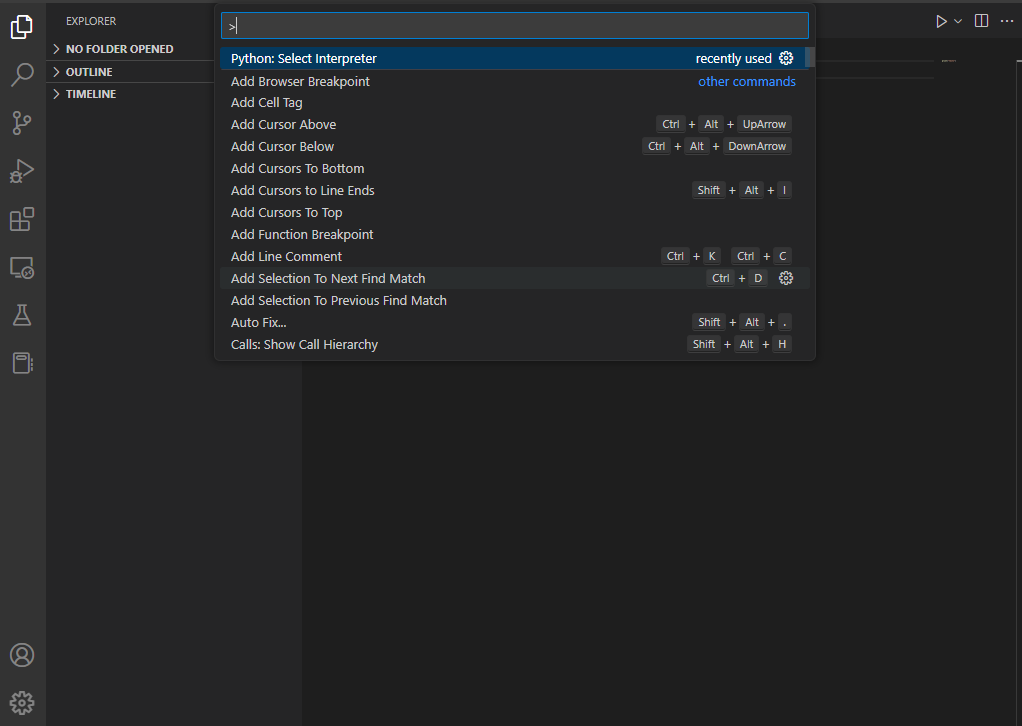
This will automatically generate a list of all of the interpreters currently available on your machine (including those provided by ActiveState). Click to select your preferred interpreter and begin working on your file.
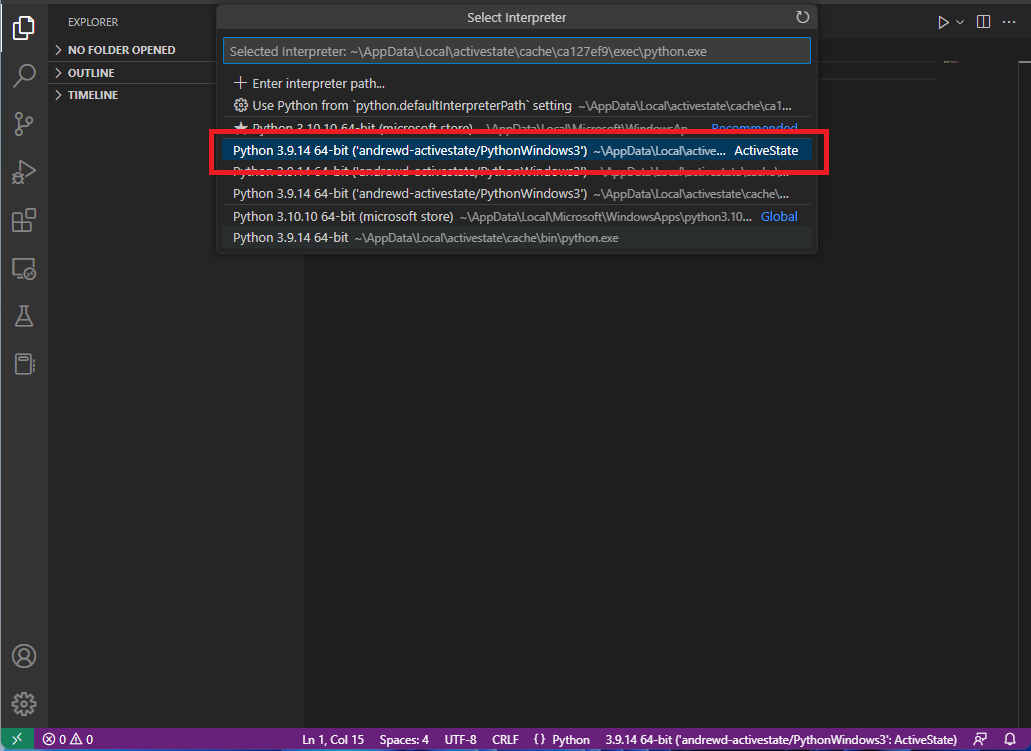
After making your selection your new interpreter will be displayed at the bottom of the VS Code window (“andrewd-activestate/PythonWindows3’:ActiveState” shown above).
Troubleshooting
If your ActiveState Python interpreter is not immediately available in the “Select Interpreter” dropdown:
- You may need to restart or update your version of VS Code.
- For Windows users, Windows Powershell is not officially supported. All State Tool commands must be made using another command terminal (Windows Terminal is preferred).
- The plugin for the extension searches for new runtimes approximately every 30 seconds, you may need to wait until your new interpreter is recognized in the system before restarting your VS Code and trying again.
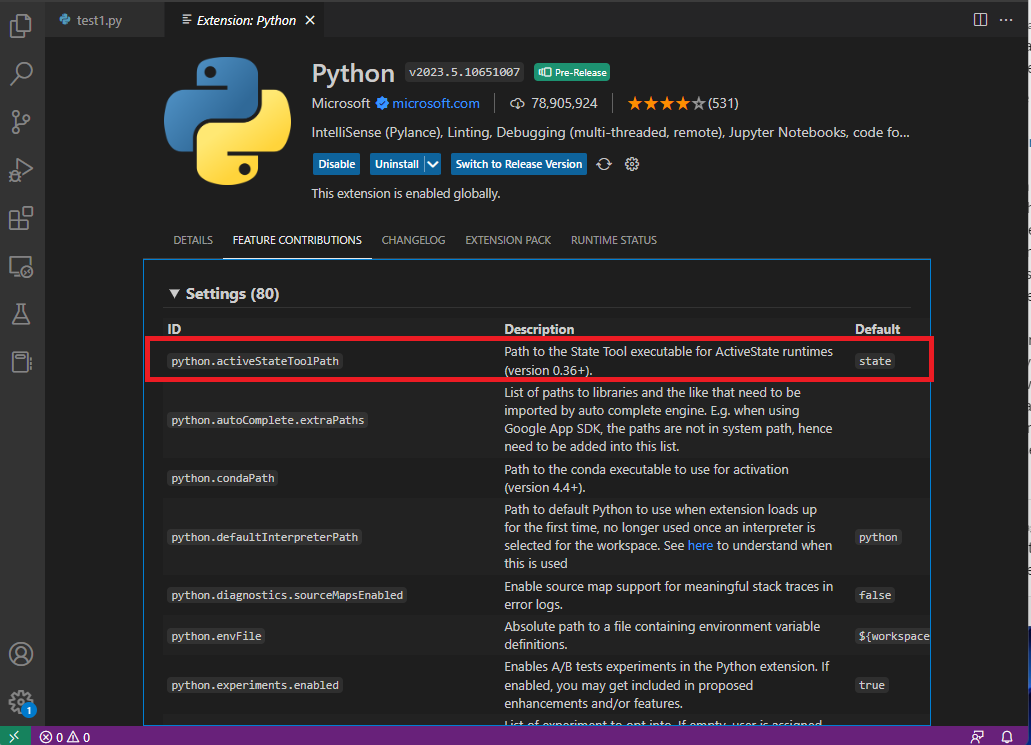
- Check that the State Tool is installed correctly in your IDE. In Visual Studio Code, go to View > Extensions > Python > Feature Contributions and look for
python.activeStateToolPathunder the “Settings” list.
- There may be a problem with the State Tool not registering on the user’s
$PATHor%PATH%variable. To enter the absolute path to the State Tool’s executable go to File > Preferences> Settings and search for ”State Tool”. Enter the absolute path to the State Tool executable in the field shown. - The Python interpreter of your project may need to be updated, as Python versions before 3.7 may not be compatible with the extension’s Python libraries. To learn more about updating your language version click here.
- You can manually enter the path to your project’s interpreter. Open a command terminal and enter
state projects
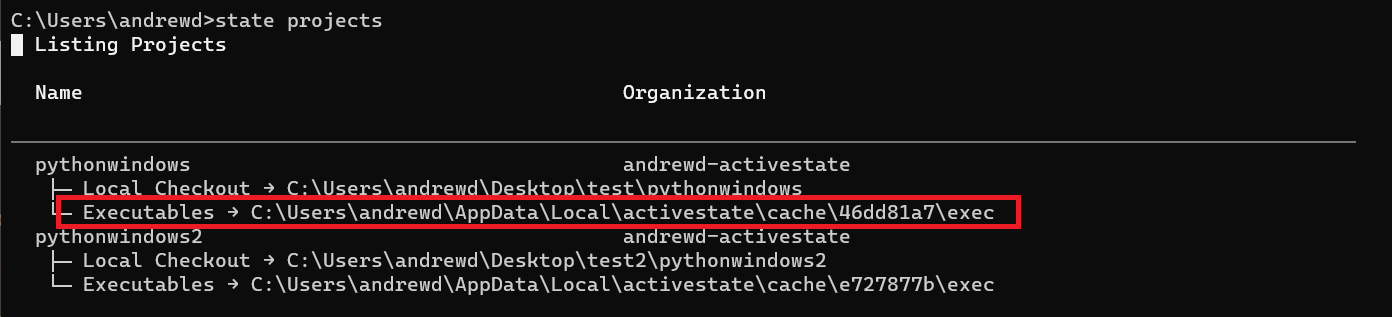
- Copy the path shown and create a new Python file or open an existing file in VS Code.
- Enter Shift + Ctrl + P on Windows and Linux (Shift + Cmd + P on macOS) to open the Command Palette and click Python: Select Interpreter > + Enter interpreter path.
- Paste the path to the executable into the field shown and press Enter.